Scoliosis In Children: Causes And Treatment
Scoliosis in children is not a very common disease, however it is an anomaly that should receive all necessary care. How to identify it? What is his treatment? We answer these questions in this article.
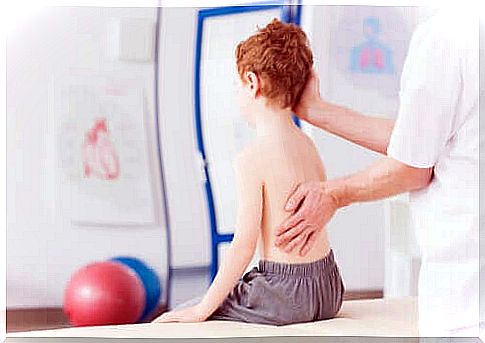
Scoliosis in children is a serious problem, which must be treated from the start. It is the name given to all the deformities of the spine that appear in children and which can have varying degrees of severity and involvement.
In general, scoliosis in children tends to get worse with growth. A deceptive aspect of this situation is that children and adolescents often tolerate this condition very well. But if the scoliosis progresses, it may require more complex treatments later on.
The most common form of scoliosis in children is “idiopathic scoliosis”. It occurs in 4 in 1,000 people. About 1% of these will be serious and require long-term treatment. In addition, children should have at least one orthopedic consultation per year, especially when they reach puberty.
What is scoliosis in children?
Scoliosis in children is defined as a deformity in the curve of the spine that occurs in younger people. This is because the spine has a curve, but it is more pronounced in some children, as if it formed a letter “C” or “S”. Sometimes this abnormality causes pain and difficulty breathing.
In the presence of scoliosis, the spine moves to one side. This can cause the bones to rotate, which can cause one shoulder or one side of the hip to be higher than the other. There are several types of scoliosis in young people:
- Infantile: it occurs in children under 3 years old and can be a birth defect or a birth defect. But sometimes it is caused by other disorders or unknown causes
- Idiopathic in adolescents: this is the most common form, it occurs in children over 10 years old. Its cause is unknown
- Juvenile: it appears in children between 3 and 10 years old and is the rarest form of this anomaly
Causes and risk factors
In most cases, the cause of childhood scoliosis is unknown. Even if we know that it affects girls more than boys. Depending on the cause, scoliosis can be classified as follows:
- Congenital scoliosis: it appears during gestation and includes several abnormalities such as the absence of vertebrae, malformations or incomplete development of the vertebrae
- Idiopathy: In these cases, the reason for scoliosis is unknown
- Neuromuscular scoliosis: it is the consequence of a neurological condition, such as muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, spina bifida, spinal cord tumors, neurofibromatosis, or paralyzing diseases
- Others: In a few cases, scoliosis in children results from infections, lesions, tumors, legs of different length or genetic diseases
Symptoms and diagnosis of scoliosis in children
Each child may have the symptoms of scoliosis differently. However, certain manifestations appear in many cases. They are as follows:
- The head is not centrally located in relation to the rest of the body
- Each arm hangs differently when the child is standing
- One of the shoulders or one of the hips is higher than the other
- If the child leans forward, one part of the back seems higher than the other
In most cases, scoliosis does not generate pain or other such symptoms. Often, the diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical observation, which is usually supplemented by an MRI. Or a computer-assisted tomography.
Treatment
Treatment for scoliosis in children depends on the age, stage of growth, the cause of the problem, the severity of the curve, and the state of health of the child. The level of tolerance to available drugs and therapies is also taken into account.
If the curve is slight or the child is approaching adolescence, a follow-up is usually put in place to watch that the abnormality does not increase. Otherwise, or when the curve is greater, the treatment chosen is often the corset. The latter prevents the curve from continuing to express itself.
Finally, if the curve is very pronounced, surgery is indicated to make the correction. This is because if a severe case is not treated, it could lead to reduced lung capacity and the development of lung disease. It is therefore a condition that deserves full attention.









