Psoriasis Of The Scalp: Symptoms And Treatment
Some studies show that among the causes of this disease there is a genetic factor.
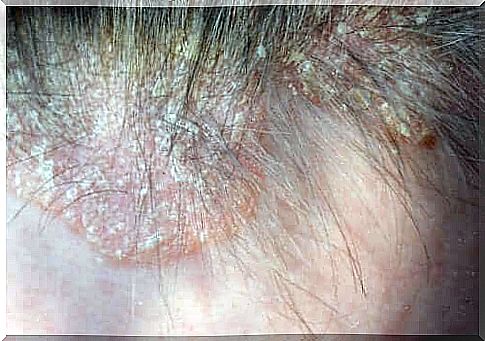
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic, recurrent inflammatory dermatosis. It is characterized by the presence of delimited erythematous plaques as well as by a white desquamation. The plaques are usually located in areas of limb folds as well as on the scalp.
Causes of scalp psoriasis
Psoriasis is considered to be a disease of great clinical variability, and for this reason, it depends on the combination of different factors.
Genetic and immune factors
Some studies show the prevalence of psoriasis in relatives of those affected. However, the development of cellular immunology indicates the involvement of leukocytes in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Environmental factors
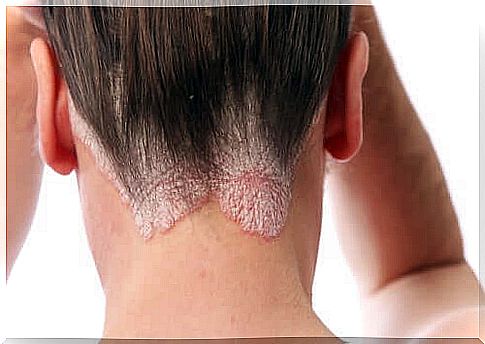
Several factors are linked to the onset or flare, especially in genetically predisposed people. Among these factors we can cite:
- Emotional stress
- Low environmental humidity
- Certain drugs
- Smoking and obesity
In addition, any skin irritation can lead to the appearance of psoriatic lesions. Stimulations such as scratching or pressing clothes can also cause or worsen existing lesions.
Medication
Regarding drugs, those that can trigger or worsen psoriasis are lithium salts, beta-blockers, antimalarials as well as abrupt stopping of corticosteroid-based treatments.
Obesity and smoking
Another important factor to take into account is obesity. Indeed, the relationship between psoriasis and obesity is a two-way street. In other words, obesity predisposes to psoriasis and psoriasis promotes obesity. As for tobacco consumption, chronic smoke inhalation alters many inflammatory processes, including the immune response.
Infectious factors
There is a relationship between infection with group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus and people who have a first outbreak of psoriasis. Especially when the push appears in the oropharynx.
What are the symptoms of scalp psoriasis?
Scalp psoriasis has a wide range of symptoms. There is indeed a great variability among the people who suffer from it, including in the same individual.
The appearance can vary from papules to large, scaly patches. Usually there is no alopecia. The area where the plaques appear most often correspond to the occipital region and the forehead.
Itching is not a typical symptom. However, scratching the plaques can lead to bleeding. In addition, the diagnosis of scalp psoriasis is based on the presence of erythematous plaques with scales.
To assess the severity of psoriasis, morphological criteria are used. One of them is the psoriasis area and severity index . This index measures the extent of lesions, the degree of erythema and scales.
Treatment

Since this is a chronic condition, the goal is to control scalp psoriasis. This area is often affected and difficult to treat.
Topical treatment
The mainstay of treatment is topical treatment. The most classic are:
- Emollients: they are used in combination with pharmacological treatment and help to maintain hydration and the good condition of the stratum corneum of the skin. This includes 20% urea, petroleum jelly, and glycerin
- Keratolytics : They are used to eliminate rough patches and promote absorption of other topical products. Salicylic acid is often used in shampoos and hair oils. The other keratolytics used are 10-30% urea, rectifying acid, sulfur and keluamide
- Coal tar: Coal tar reduces the thickness of the skin. It is indicated in children and in stable plaques. Although it does not exhibit systemic toxicity, it can be irritating.
- Topical corticosteroids: This is the treatment of choice for mild cases. These drugs have anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive action
Systemic treatment of scalp psoriasis
It is used in cases where topical treatment does not respond satisfactorily. Among the various drugs we can mention:
- Methotrexate: this medication is indicated in moderate and severe forms of psoriasis
- Cyclosporine: this is an immunosuppressant that inhibits the production of T-dependent antibodies
- Acitretin: it is a derivative of vitamin A. It has an inhibitory effect on psoriasis, including keratolytic disorders